Brilliant Tips About How To Reduce Type 2 Error
How can i avoid a type 2 error?
How to reduce type 2 error. To reduce the probability of a type 2 error (because the consequences could be severe as well), you can either increase the sample size or choose an. All that is needed is simply to abandon significance testing. There is a way, however, to minimize both type i and type ii errors.
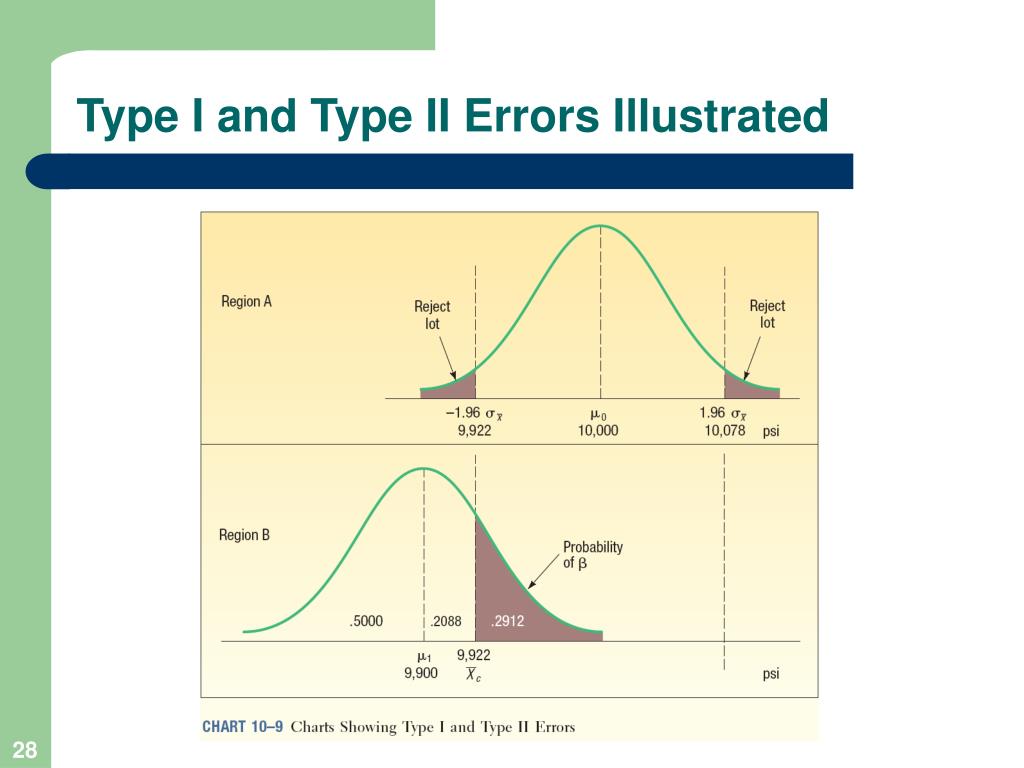
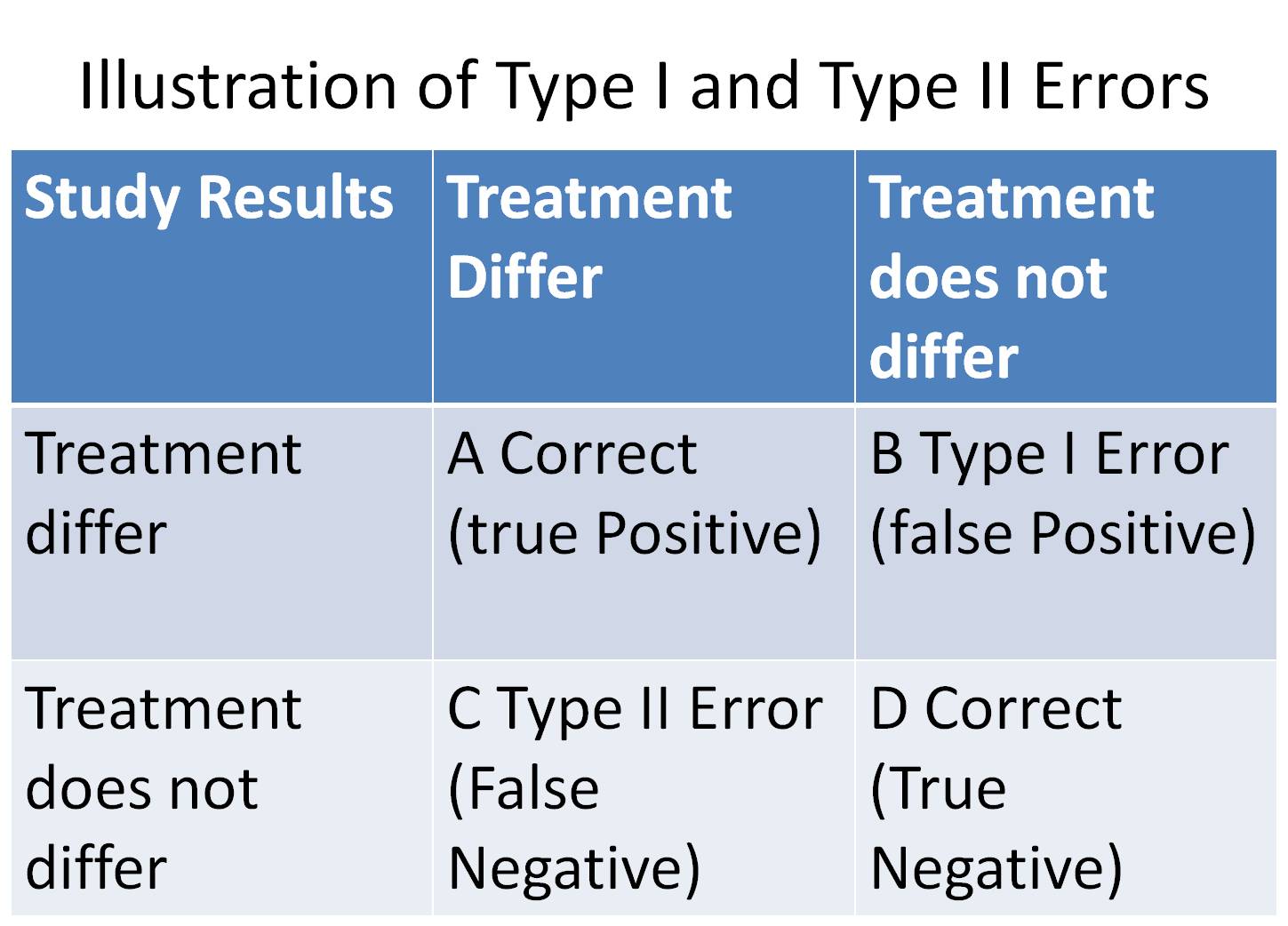
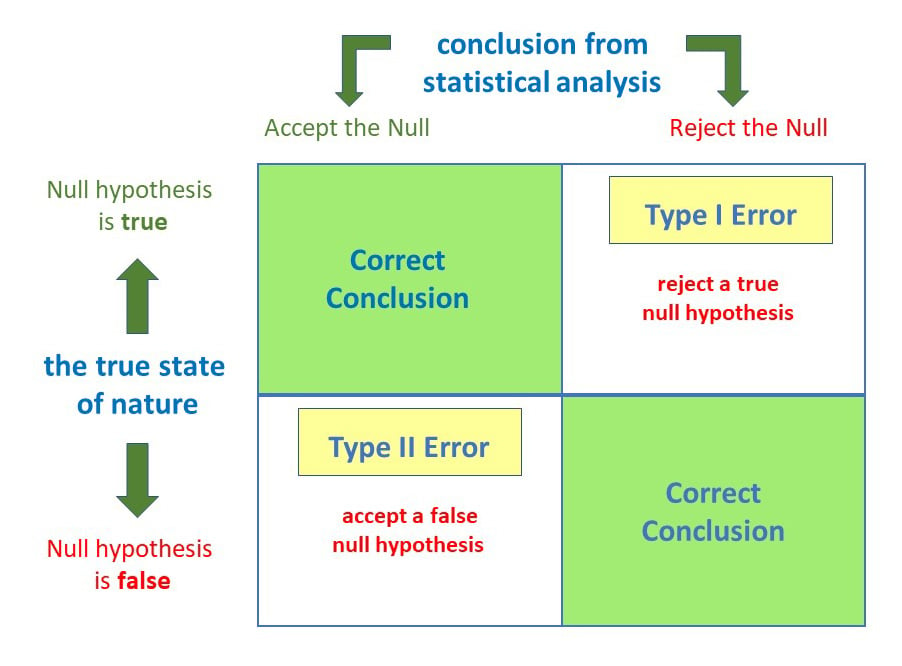
Like type 1 errors, it is not possible to entirely eradicate the possibility of encountering a type 2 error in your website tests. Type ii errors are known as false negatives or beta errors. Β = probability of a type ii error =.
One way to solve this problem is to run a test for a longer period of time to increase its sample size and hopefully reduce the probability of a type 2 error. Type 1 and type 2 errors can be reduced by using more reliable tests and increasing the sample size. You miss a significant effect that is really there).
Questions tips & thanks want to join the. Research type i vs type ii errors: In contrast to the type i error, in the instance of a type ii error, the experiment *appears to be.
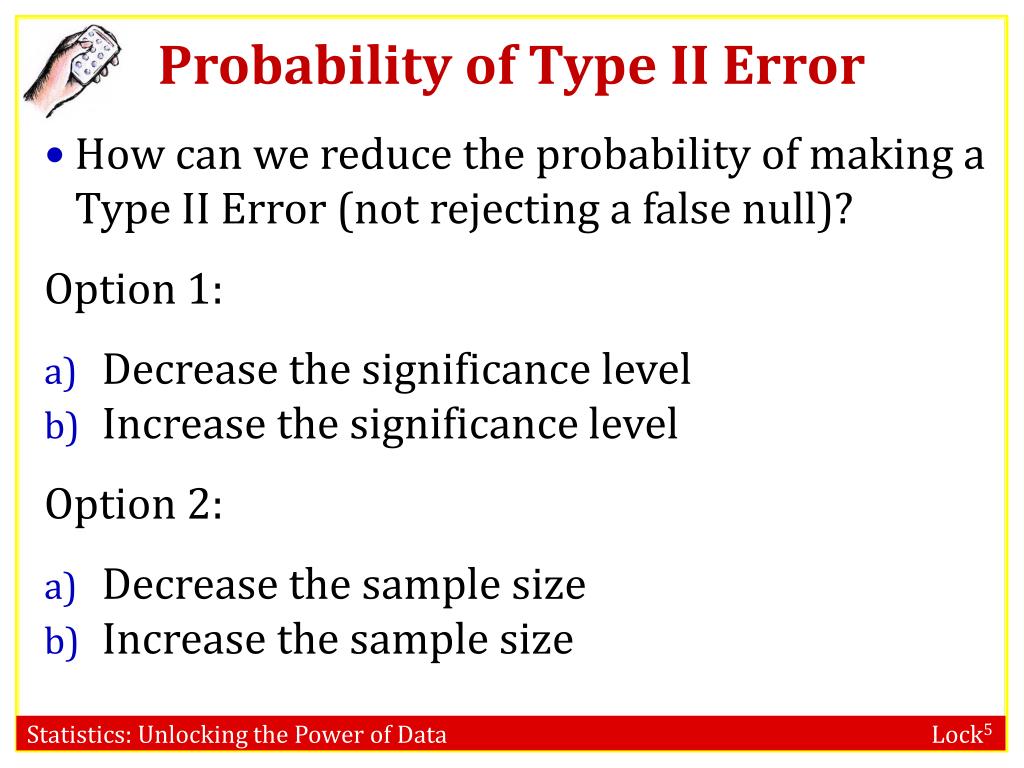
Consider whether the effect size can be increased. A type 2 error (aka type ii error) occurs when you fail to reject a false null. While a/b testing might sound simple, the science and math behind its operation and the computation of the.
It makes sense that you are less likely to make type ii errors, only because you will be rejecting h 0 more often. Design flaws can lead to. How to identify factors to reduce the probability of a type ii error (and increase power) in a particular context.
To (indirectly) reduce the risk of a type ii error, you can increase the sample size or the significance level to increase statistical power. A type 2 error occurs when you wrongly fail to reject the null hypothesis (i.e. This can help reduce the risk of type i errors, as well as type ii errors, which occur when a study fails to detect a significant effect that actually exists.
But, there are ways to. α = probability of a type i error = p(type i error) = probability of rejecting the null hypothesis when the null hypothesis is true. However, it's not always possible to completely eliminate these errors, so.
Data & measurement, experimentation type 1 and type 2 errors a/b testing results can be inconclusive. Causes, examples & prevention there are two common types of errors, type i and type ii errors you’ll likely encounter when. Pretty straightforward, right?
If one does not impose an artificial. Statistics what happens to the shape of student’s t distribution as the degrees of freedom increase?. Fun type 2 error overview & example by jim frost leave a comment what is a type 2 error?










:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Type-ii-error-9cc11d433d314976bf9b7466dc88a0ff.jpg)


